
When it comes to international trade and customs, understanding classification systems for goods is crucial. One such system is the HSIC code — short for Harmonized System Identification Code. This code plays a vital role in categorizing products in a standardized way across countries, ensuring smooth customs clearance and correct application of tariffs and taxes.
Many businesses, importers, exporters, and logistics professionals often encounter confusion around what exactly an HSIC code is, how it differs from other codes like HS or HSN, and why it matters so much. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the HSIC code by explaining its meaning, structure, usage, and how you can find the correct code for your products.
Understanding the HSIC classification system can save your business time and money by preventing shipment delays, avoiding customs penalties, and ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. Whether you are new to international trade or looking to deepen your knowledge, this article will provide you with all the information you need about HSIC codes.
In the sections ahead, you’ll learn:
- The exact definition and purpose of HSIC codes
- How the HSIC code system impacts customs duties and tariffs
- Practical steps for HSIC code lookup
- How to avoid costly errors with proper HSIC classification
By the end of this guide, you’ll be confident in using HSIC codes correctly, optimizing your import/export processes, and complying with customs regulations effectively.
The term HSIC code stands for Harmonized System Identification Code. It is part of an internationally standardized system used to classify traded products. This system was developed and is maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO) to provide a uniform way of naming and numbering goods across different countries. The HSIC code helps customs authorities, traders, and governments quickly identify the nature of a product, which is essential for applying tariffs, regulations, and trade policies.
The HSIC system is closely related to the more commonly known HS code (Harmonized System code), and in some regions, the terms may be used interchangeably. However, the HSIC code often refers specifically to identification numbers assigned within this system, sometimes including additional digits or classifications used by specific countries or customs unions. For example, India uses the HSN code (Harmonized System Nomenclature), which is similar but tailored to Indian tariff structures.
Understanding the exact meaning of the HSIC code is important because it determines how your products are treated when crossing international borders. Misinterpretation or incorrect classification can lead to customs delays, unexpected fines, or increased taxes. On the other hand, accurate HSIC classification streamlines customs clearance, ensures compliance with trade laws, and helps businesses avoid costly mistakes.
In comparison to related codes like HS and HSN, the HSIC code can be seen as an identifier that fits within the broader harmonized classification system. While HS codes typically contain six digits that describe the product category globally, HSIC codes may include additional numbers for more precise identification used by specific customs authorities. This distinction helps tailor the classification to local tariff schedules while maintaining consistency with global standards.
Knowing the differences between these codes is essential for businesses engaged in international trade, as each country might require specific codes when submitting customs documents. For example, when importing goods into the United States, businesses primarily use the HS code system, while in other countries, like India or Canada, local variations or extensions of the HSIC code are common.
In short, the HSIC code meaning is tied to its function as a standardized numeric system that classifies traded products worldwide, allowing customs officials to identify goods, apply the correct duties, and regulate imports and exports efficiently.
HSIC codes play a crucial role in international trade by providing a universal language for categorizing products. This standardized classification system helps governments, customs authorities, and businesses across the globe understand exactly what is being shipped, bought, or sold. The main purpose of HSIC codes is to ensure that goods are identified accurately, so the right customs duties, taxes, and regulations can be applied consistently.
One of the primary reasons HSIC codes are important is because they directly impact import and export duties. Customs authorities rely on these codes to determine how much tax to charge on incoming shipments. A product’s HSIC classification can mean the difference between paying a low tariff or a high tariff, which significantly affects a company’s bottom line. Misclassifying a product can lead to overpayment or costly penalties for underpayment, so accuracy is essential.
Additionally, HSIC codes assist in enforcing trade policies. Governments use these codes to monitor the flow of goods in and out of their countries. This allows them to track imports and exports, ensure compliance with international agreements, and apply trade restrictions or embargoes where necessary. For example, if certain products are subject to export bans or quotas, customs officials can easily identify them using their HSIC codes.
The use of HSIC codes also speeds up the customs clearance process. Since the code instantly informs customs officers about the type of goods in a shipment, it reduces the need for lengthy inspections or paperwork checks. This efficiency helps businesses save time and avoid delays, ensuring products reach their destinations quickly.
Moreover, HSIC codes are critical for statistical purposes. Governments collect trade data based on these codes to analyze market trends, calculate trade balances, and make informed economic decisions. Accurate classification feeds into reliable trade statistics, which benefit policymakers, economists, and business strategists.
Here is a simple table summarizing the main purposes and benefits of HSIC codes:
| Purpose | Benefit to Stakeholders |
|---|---|
| Accurate product classification | Ensures correct duties and taxes are applied |
| Customs clearance efficiency | Speeds up import/export processes |
| Trade policy enforcement | Helps monitor and regulate trade restrictions |
| Reliable trade statistics | Informs government economic planning and decision-making |
In conclusion, HSIC codes are indispensable for facilitating smooth and lawful international trade. They ensure products are consistently classified, which supports correct taxation, efficient customs processing, trade compliance, and valuable market insights. Businesses that understand and correctly use HSIC codes can reduce risks, avoid penalties, and enhance their global trade operations.
How to Find Your HSIC Code: A Step-by-Step HSIC Code Lookup Guide
Finding the correct HSIC code for your product is essential to ensure smooth customs clearance and accurate duty payment. However, the process can sometimes be confusing due to the vast number of codes and detailed classification criteria. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you perform an accurate HSIC code lookup.
Step 1: Understand Your Product in Detail
Before searching for the HSIC code, gather all relevant information about your product. This includes its composition, function, material, and intended use. The more precise your product description, the easier it is to identify the correct code. For example, “cotton T-shirts” and “synthetic fiber T-shirts” fall under different HSIC classifications.
Step 2: Use Official Customs or Trade Authority Websites
Most countries provide official HSIC or HS code lookup tools on their customs or trade authority websites. These portals allow you to search by keyword or browse categories to find the matching code. For instance:
- The World Customs Organization (WCO) website offers the global Harmonized System database.
- The U.S. International Trade Commission provides an HS code search tool for imports into the United States.
- Many countries have their own portals with specific HSIC extensions or local code systems.
Step 3: Use Online HSIC Code Lookup Tools
There are several third-party websites and software tools designed to simplify HSIC code searches. These tools let you enter your product’s name or description and provide a list of potential HSIC codes with explanations. Examples include:
- TradeTariff (UK)
- Customs Info Database
- Import Genius
Step 4: Consult Customs Brokers or Trade Experts
If you’re unsure or your product is complex, consulting a customs broker or a trade compliance expert can be very helpful. These professionals have experience classifying goods correctly and can guide you to the exact HSIC code that fits your product, reducing the risk of misclassification.
Step 5: Cross-Verify with Product Samples and Regulations
Once you have a tentative HSIC code, double-check it by reviewing your product’s technical specifications against the classification notes and tariff schedules. HSIC codes come with detailed explanatory notes and legal interpretations that help clarify borderline cases.
Tips for Accurate HSIC Code Lookup
- Avoid vague descriptions. Be as specific as possible about your product.
- Check for updates. HSIC codes and their classifications are periodically revised. Make sure you use the latest version.
- Consider all product uses. Sometimes the classification depends on the product’s primary function or packaging.
Why Getting the Right HSIC Code Matters
Choosing the wrong HSIC code can have serious consequences, including shipment delays, customs fines, or unexpected tariffs. According to a 2022 study by the International Chamber of Commerce, incorrect product classification accounts for over 30% of customs disputes globally. Therefore, investing time and effort into accurate HSIC code lookup protects your business from costly disruptions.
HSIC Code Structure Explained: Understanding the Format and Digits
The HSIC code is designed as a hierarchical numeric system that helps classify goods with increasing specificity at each level. Understanding the structure of the HSIC code is key to correctly identifying your product’s classification and ensuring compliance with customs regulations.
Breakdown of the HSIC Code Format
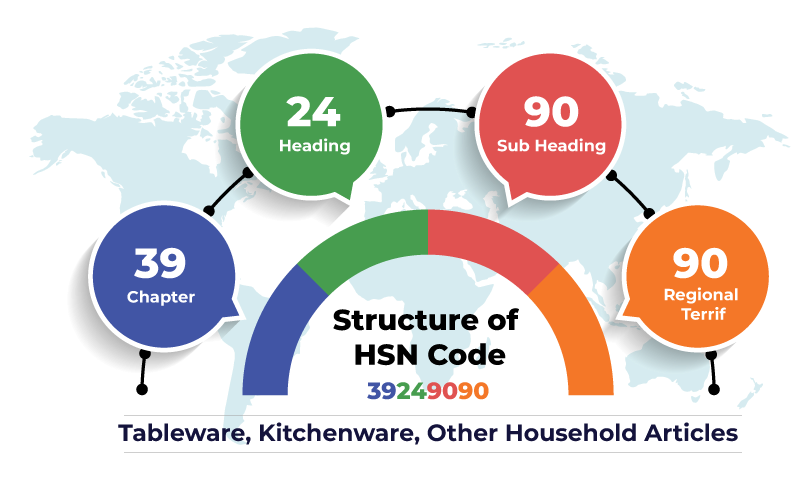
Typically, an HSIC code consists of 6 digits, divided into segments that each provide more detailed information about the product:
| Digits | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | Chapter – Broad category | 09 = Coffee, tea, spices |
| 3-4 | Heading – Product group within chapter | 09 03 = Coffee, roasted |
| 5-6 | Subheading – Specific product details | 09 03 10 = Coffee, roasted, not decaffeinated |
These six digits form the global HS code recognized worldwide. Some countries add extra digits to the HSIC code to specify tariff or tax categories more precisely for local use. For instance, India’s HSN code extends to 8 digits to capture finer distinctions for customs and GST purposes.
Why the Structure Matters
The hierarchical structure allows customs authorities to:
- Quickly identify the general product category (chapter).
- Narrow down to specific product types (heading).
- Determine precise product details that impact duties (subheading).
This layered approach ensures that products are not just broadly classified but also accurately categorized, which affects tariff rates, trade policies, and import/export restrictions.
Example of HSIC Code Application
Let’s take cotton T-shirts as an example:
- Chapter 61 covers “Articles of apparel and clothing accessories.”
- Heading 6109 specifically refers to “T-shirts, singlets and other vests, knitted or crocheted.”
- Subheading 6109.10 refers to “T-shirts, singlets and other vests, of cotton.”
This means the HSIC code 6109.10 precisely classifies cotton T-shirts for customs, helping determine the applicable duties and regulations.
Additional Notes on HSIC Code Structure
- Some product categories can have multiple subheadings depending on characteristics like material, processing method, or end-use.
- Customs authorities use explanatory notes to interpret HSIC codes and resolve classification ambiguities.
- It’s important to reference the latest official HS tariff book or database when assigning codes, as classifications can change.
Summary Table: HSIC Code Structure
| Segment | Description | Number of Digits | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chapter | Broad product category | 2 | General classification |
| Heading | Product group within chapter | 2 | Narrowing down classification |
| Subheading | Specific product details | 2 | Precise product description |
| Local Extension (optional) | Additional country-specific digits | Varies | Further detail for national tariffs |
Understanding this structure helps businesses classify their products properly and avoid costly customs mistakes. It also makes international communication about goods smoother, reducing delays and disputes in cross-border trade.
Difference Between HSIC Code, HS Code, and HSN Code
Navigating international trade terminology can be confusing, especially with codes like HSIC code, HS code, and HSN code all sounding similar but having distinct uses. Understanding the difference between these terms is essential for correctly classifying products and complying with customs requirements.
HS Code (Harmonized System Code):
This is the internationally recognized 6-digit classification system developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). The HS code is the foundation for identifying traded goods worldwide. Every country uses this base 6-digit code to classify products for customs duties, import/export regulations, and trade statistics.
HSIC Code (Harmonized System Identification Code):
The HSIC code often refers to the HS code along with any country-specific extensions or identifiers used for finer classification. In some countries, HSIC codes include additional digits beyond the standard 6 to reflect local tariff rules or tax categories. It is a more specific form of the HS code, tailored to individual countries’ customs systems but still rooted in the global Harmonized System framework.
HSN Code (Harmonized System Nomenclature Code):
The HSN code is a term commonly used in India and some other countries to describe their adaptation of the HS code system. It generally consists of 8 digits instead of 6, allowing for more detailed classification specific to local taxation and customs duties. For example, India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) system heavily relies on the HSN code for product classification.
| Code Type | Digits | Usage | Region/Application | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HS Code | 6 | International trade classification | Global | Base code used worldwide |
| HSIC Code | 6+ (extended) | Country-specific classification | Varies by country | Includes extensions for local customs |
| HSN Code | 8 | Local classification for tax/customs | Primarily India and some countries | Used for GST and detailed tariff rules |
Why Does This Matter?
The distinction is important because using the wrong code format can cause customs delays or penalties. For example, when importing into India, providing only the 6-digit HS code might not be sufficient — the full 8-digit HSN code is required for correct GST processing. Similarly, some countries expect their own HSIC extensions alongside the base HS code.
Practical Example
- A shipment of electronic devices classified under HS code 8517 (for phones) may have an HSIC code with added digits in a specific country that breaks down types of phones or accessories for tariff purposes.
- In India, the same product would have an 8-digit HSN code like 8517.12.00, specifying more exact product details for customs and GST.
In summary, while these codes are all related, the HS code is the universal base, the HSIC code adds local specificity, and the HSN code is a country-specific system that often builds upon the HS code with additional detail.
Common Uses of HSIC Code in Business and Trade
The HSIC code serves multiple important purposes across various sectors involved in international trade. Its practical uses go far beyond simple product classification and directly impact several key business functions. Understanding these common applications can help businesses leverage HSIC codes effectively and stay compliant with trade regulations.
1. Customs Clearance and Import/Export Documentation
One of the primary uses of the HSIC code is in customs declarations. When importing or exporting goods, businesses must provide the correct HSIC code on shipping documents, invoices, and customs forms. This enables customs officials to:
- Identify the products being shipped
- Apply the correct tariff or duty rates
- Ensure compliance with import/export restrictions
Incorrect or missing HSIC codes can cause shipments to be delayed, held for inspection, or even rejected at customs, leading to increased costs and lost business opportunities.
2. Determining Tariffs and Duties
Customs authorities use HSIC codes to calculate the applicable import duties and tariffs on products. Since tariffs vary by product category, accurate HSIC classification directly affects the cost of bringing goods into a country. For example, raw materials may have lower tariffs compared to finished goods, and HSIC codes help differentiate between them.
3. Compliance with Trade Regulations
HSIC codes also help enforce trade policies and restrictions. Many countries restrict or regulate the import and export of certain goods, such as hazardous materials, agricultural products, or dual-use technologies. Customs officials use HSIC codes to identify such items and apply necessary controls or documentation requirements.
4. Trade Data and Market Analysis
Governments and businesses analyze international trade statistics collected based on HSIC codes. This data helps in:
- Monitoring trade balances and trends
- Identifying growth markets and sectors
- Making informed policy decisions
Businesses can use trade data tied to HSIC codes to develop market strategies and identify emerging opportunities.
5. Inventory Management and Classification
Some companies use HSIC codes internally to classify and organize inventory, especially if they deal with a wide variety of products internationally. This systematized approach improves supply chain visibility and reporting accuracy.
Case Study: How Correct HSIC Classification Saved Costs for a Manufacturing Company
A manufacturing company importing electronic components faced frequent customs delays and unexpected tariffs. After consulting a trade expert, they realized their HSIC codes were incorrectly assigned, leading to higher duty rates. By reclassifying products with accurate HSIC codes, the company:
- Reduced import duties by 15%
- Avoided customs delays, cutting clearance time by 30%
- Improved compliance, preventing penalties
This case highlights how proper HSIC code use can yield tangible financial and operational benefits.
Summary of HSIC Code Uses
| Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Customs clearance | Faster processing and fewer shipment delays |
| Tariff determination | Accurate duty calculation and cost savings |
| Trade regulation compliance | Avoid fines and legal issues |
| Trade data analysis | Strategic business insights |
| Inventory classification | Better internal management and reporting |
The HSIC code is more than just a number — it’s a powerful tool that influences many aspects of global trade and business operations. Using it correctly helps companies stay competitive and compliant in the complex world of international commerce.
Common Challenges and Tips for Accurate HSIC Code Classification
While HSIC codes are essential for smooth international trade, correctly classifying products can be complex and challenging. Many businesses face common pitfalls that lead to misclassification, resulting in delays, fines, or additional costs. Understanding these challenges and how to address them is critical for effective HSIC code use.
Common Challenges
- Complex Product Composition
Many modern products contain multiple materials or components, making classification difficult. For example, electronic devices with plastic, metal, and software elements may fit into several HSIC categories. Deciding which material or function takes precedence requires careful analysis. - Lack of Clear Product Descriptions
Incomplete or vague product descriptions can cause confusion during HSIC code assignment. Without precise information about the product’s use, composition, or manufacturing process, it’s easy to pick the wrong code. - Frequent Updates to HSIC Codes
The Harmonized System is updated every five years by the World Customs Organization to reflect new products and trade developments. Businesses must stay current with these changes to avoid using outdated codes. - Differences in National Extensions
Since many countries add their own digits or classifications to the base HSIC code, businesses operating internationally must understand local variations. This complexity can lead to errors if only the base HS code is used without country-specific adjustments. - Discrepancies Between Importer and Exporter Classification
Sometimes, importers and exporters classify the same product differently, leading to customs disputes and shipment delays. Harmonizing these classifications is important for smoother transactions.
Tips for Accurate HSIC Code Classification

- Consult Official Tariff Guide
Always refer to your country’s official customs tariff book or website for the latest HSIC code information and guidelines. - Use Detailed Product Information
Provide as much detail as possible about the product, including material composition, function, and manufacturing process. - Seek Expert Advice
For complex products, consider hiring customs brokers or trade compliance consultants who specialize in HSIC classification. - Stay Updated on Changes
Regularly review updates from the World Customs Organization and national customs authorities to keep your HSIC codes current. - Use Technology Tools
Leverage online HSIC code lookup tools and classification software to improve accuracy and efficiency. - Maintain Consistency in Documentation
Ensure that all parties involved in the trade (exporters, importers, freight forwarders) agree on the HSIC code to prevent discrepancies.
Quick Checklist for Accurate HSIC Code Assignment
- Gather detailed product descriptions and specifications
- Cross-check HSIC code with official customs tariff publications
- Confirm local country-specific code extensions
- Review recent changes or updates to HSIC codes
- Consult with customs experts if unsure
- Document and communicate the chosen HSIC code internally and with trade partners
By addressing these challenges proactively and following best practices, businesses can minimize errors, speed up customs clearance, and avoid costly penalties related to HSIC code misclassification.
Frequently Asked Questions About HSIC Code
What is an HSIC code?
The HSIC code (Harmonized System Identification Code) is a numerical system used worldwide to classify traded products. It helps customs and trade authorities identify goods, apply tariffs, and regulate imports and exports efficiently.
How do I find the correct HSIC code for my product?
To find your HSIC code, start by gathering a detailed description of your product. Use official customs websites or trusted HSIC lookup tools, and if necessary, consult with customs brokers or trade experts to ensure accuracy.
Is HSIC code the same as HS code?
The HS code is the standard 6-digit classification used internationally. The HSIC code often refers to the HS code plus any additional country-specific extensions used for more detailed classification.
What is the difference between HSIC code and HSN code?
HSN code is a localized version of the HS code used primarily in India. It typically has 8 digits to capture more detailed product information for taxation and customs purposes, whereas the HSIC code can include local extensions but is based on the global 6-digit HS code.
Why is the HSIC code important for international trade?
HSIC codes ensure goods are correctly classified, which affects customs duties, import/export regulations, and trade compliance. Correct classification helps avoid delays, fines, and extra costs.
Can HSIC codes change over time?
Yes, the World Customs Organization updates the Harmonized System every five years to include new products and reflect changing trade patterns. Businesses must stay updated on these changes.
What happens if I use the wrong HSIC code?
Using an incorrect HSIC code can result in customs delays, fines, higher tariffs, or shipment rejections. It can also damage your business’s reputation and increase costs.
Are HSIC codes the same worldwide?
The base 6-digit HS code is standardized internationally. However, many countries add extra digits or modify classifications for local needs, resulting in HSIC codes that may vary slightly by country.
How often should I review my HSIC codes?
It’s best to review your HSIC codes regularly, especially when product lines change or when there are updates announced by customs authorities or the World Customs Organization.






